VBAP Panner
Ardour's VBAP panner is currently in development, and its semantics may
change in the near future, possibly affecting mixes using it. It is advised not
to rely on it for important production work while the dust settles.
The Panner only works in fixed static mode, it does not support
automation playback.
VBAP is a versatile and straightforward method to pan a source around over an arbitrary number of speakers on a horizontal polygon or a 3D surface, even if the speaker layout is highly irregular.
Basic concepts
VBAP was developed by Ville Pulkki at Aalto University, Helsinki, in 1997. It works by distributing the signal to the speakers nearest to the desired direction with appropriate weightings, aiming to create a maximally sharp phantom source by using as few speakers as possible:
- one speaker, if the desired direction coincides with a speaker location,
- two speakers, if the desired direction is on the line between two speakers,
- and three speakers in the general 3D case.
Thus, if the panner is moved onto a speaker, only this speaker will get any signal. This is handy when precise 1:1 routing is needed.
The drawback of VBAP is that a moving source will constantly change its apparent sharpness, as it transitions between the three states mentioned above.
An horizontal VBAP panner has one parameter, the azimuth angle. A full-sphere panner offers an additional elevation angle control.
More elaborate implementations of VBAP also include a spread parameter, which will distribute the signal over a greater number of speakers in order to maintain constant (but no longer maximal) sharpness, regardless of position. Ardour's VBAP panner does not currently include this feature.
Speaker layout
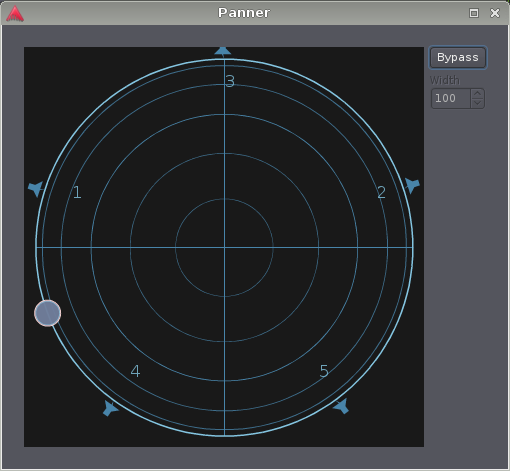
Each VBAP panner is specific to its speaker layout—the panner has to "know" about the precise location of all the speakers. A complete VBAP implementation must therefore include the possibility to define this layout.
Ardour currently uses a simplified approach: if a track or bus has more than two output channels (which implies stereo), it assumes that there are N speakers distributed in a regular N-gon. That means that for irregular layouts such as 5.1 or 7.1, the direction dialed in will differ a bit from the actual auditory result, but any desired spatialisation can still be achieved.
Experimental 3D VBAP
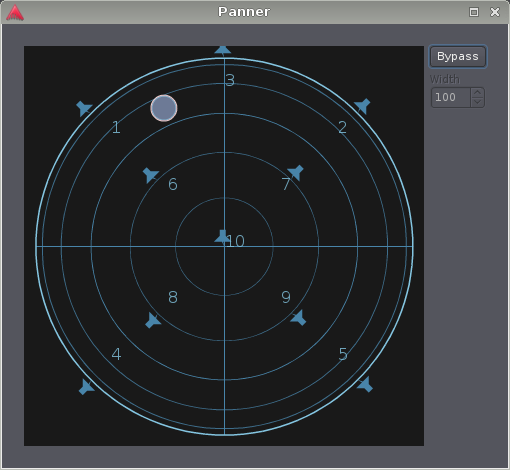
For tracks with 10 outputs, Ardour will currently assume a 3-dimensional speaker layout corresponding to Auro-3D 10.1, which is a horizontal 5.1 system, four elevated speakers above L, R, Ls, and Rs, and an additional "voice-of-god" speaker at the zenith.
N:M panning
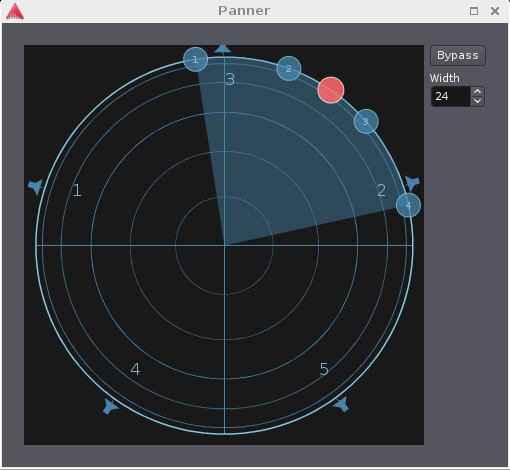
For tracks and busses with more than one input, Ardour will (for now) assume that the inputs are distributed symmetrically along the latitude around the panner direction. The width parameter controls the opening angle of the distribution sector.
